https://www.jianshu.com/p/28fba43ac0b0
1.1.1. Android消息机制
Android 线程间通信的方式?
- Handler
- 共享内存(变量)
- 文件 数据库
- Java 里的 wait(),notify(),notifyAll()
多个Handler 一个Looper 一个MsgQueue 多个Msg
Handler
构造方法绑定Looper中的 MessageQueue
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
- sendMessage(Message msg)
- sendEmptyMessage(int what)
- sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0)
- sendEmptyMessageDelayed(what, 0)
以上均等于
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}
Looper
ActivityThread的main方法中初始化looper
public static void main(String[] args) {
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
MessageQueue.java
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {
if (msg.target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Message must have a target.");
}
if (msg.isInUse()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(msg + " This message is already in use.");
}
synchronized (this) {
if (mQuitting) {
IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException(
msg.target + " sending message to a Handler on a dead thread");
Log.w(TAG, e.getMessage(), e);
msg.recycle();
return false;
}
msg.markInUse();
msg.when = when;
Message p = mMessages;
boolean needWake;
if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {
// New head, wake up the event queue if blocked.
msg.next = p;
mMessages = msg;
needWake = mBlocked;
} else {
// Inserted within the middle of the queue. Usually we don't have to wake
// up the event queue unless there is a barrier at the head of the queue
// and the message is the earliest asynchronous message in the queue.
needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous();
Message prev;
for (;;) {
prev = p;
p = p.next;
if (p == null || when < p.when) {
break;
}
if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) {
needWake = false;
}
}
msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.next
prev.next = msg;
}
// We can assume mPtr != 0 because mQuitting is false.
if (needWake) {
nativeWake(mPtr);
}
}
return true;
}
腾讯Android面试:Handler中有Loop死循环,为什么没有阻塞主线程,原理是什么
Handler中有Looper死循环,为什么没有阻塞主线程?
ActivityThread创建时会初始化Looper,线程执行代码后,生命周期变会终止。所以我们需要Looper死循环才能保证主线程一直存活。
主线程的死循环一直运行是不是特别消耗CPU资源呢?
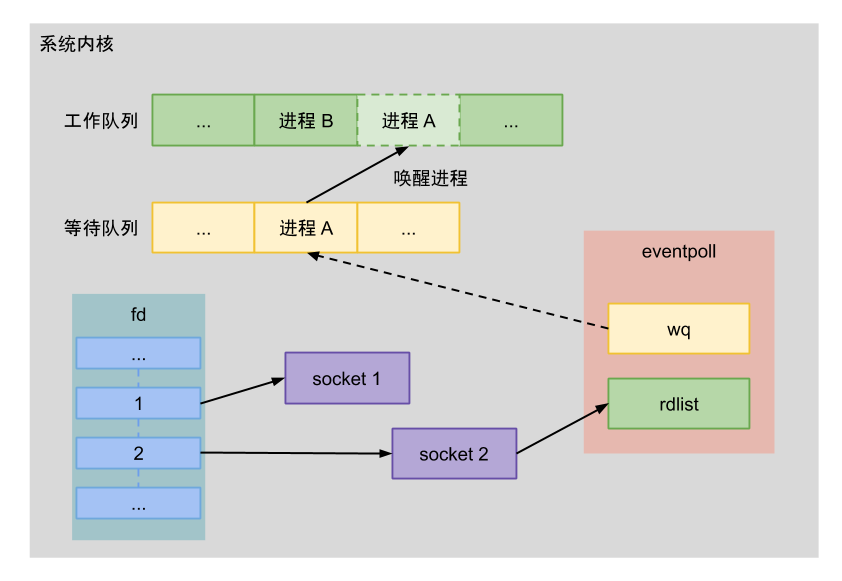
其实不然,这里就涉及到Linux pipe/epoll机制,简单说就是在主线程的MessageQueue没有消息时,便阻塞在loop的queue.next()中的nativePollOnce()方法里,此时主线程会释放CPU资源进入休眠状态,直到下个消息到达或者有事务发生,通过往pipe管道写端写入数据来唤醒主线程工作。这里采用的epoll机制,是一种IO多路复用机制,可以同时监控多个描述符,当某个描述符就绪(读或写就绪),则立刻通知相应程序进行读或写操作,本质同步I/O,即读写是阻塞的。 所以说,主线程大多数时候都是处于休眠状态,并不会消耗大量CPU资源。 Gityuan–Handler(Native层)
MessageQueue中的msg是根据什么排列的?
为什么handler可以在线程间传递?
Handler创建的时候会采用当前线程的Looper来构造消息循环系统。 构造方法中会取looper,该looper是ActivityThread初始化时候创建的,并保存在ThreadLocal中
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) {
final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass();
if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) &&
(klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) {
Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " +
klass.getCanonicalName());
}
}
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread " + Thread.currentThread()
+ " that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}